In this Article
Increasingly, users are turning to proxies to manage their workflows with more security, flexibility, and anonymity. When you start incorporating this powerful tool into your online routine, some questions may arise. In this article, we’ll reveal the answer to the key differences between using a host-based proxy versus directly connecting through an IP address.
What is a Host IP?
It is a specific IP address that is associated with a domain or server. Domain is the name of a website that you type into your browser’s address bar to visit it. Domain names were created to eliminate the need to remember a numeric IP address which is a series of four numbers separated by dots that identifies the server where the website is hosted.
So, how does it work? Instead of an IP address, you use a domain name such as gw.dataimpulse.com or others. With this approach, IPs can rotate dynamically, ensuring greater stability while the provider updates them without requiring any configuration changes on your end. The system automatically assigns a new IP with each request.
One of the distinctive features is that if one backend IP goes down, the host can redirect traffic to another working IP.
Connecting via host can have some pros and cons, let’s consider the main ones:
✅ Advantages:
-
- Automatic IP hostname switching. It helps maintain proxy uptime by changing to a new IP if a server fails.
- Geo-location load balancing for clients from different countries. Some providers implement DNS-based filtering or geolocation-based routing.
- Smart choice for high-volume data collection tasks. Large organizations use domain-based proxies to route employees’ internet traffic and adjust IPs for load balancing. It prevents bottlenecks and improves connection reliability.
- Ease of use. It’s simpler to use a domain name.
❌ Disadvantages:
- DNS blocking risk. Some countries, like China, might restrict access to certain domains.
- Potential slowdowns from DNS resolution. Since these proxies rely on DNS resolution, there’s a slight delay because the system first has to resolve the domain name.
Domain-based proxies (host IPs) are especially useful for web scraping, SEO monitoring, and social media management, where frequent IP changes help protect user identity and comply with usage policies.
What is a Direct IP?
It means connecting directly to a server using its specific IP address without using a domain name. Instead of relying on a domain (e.g., “gw.dataimpulse.com“), you connect using the raw numeric IP address like 105.117.1.1.
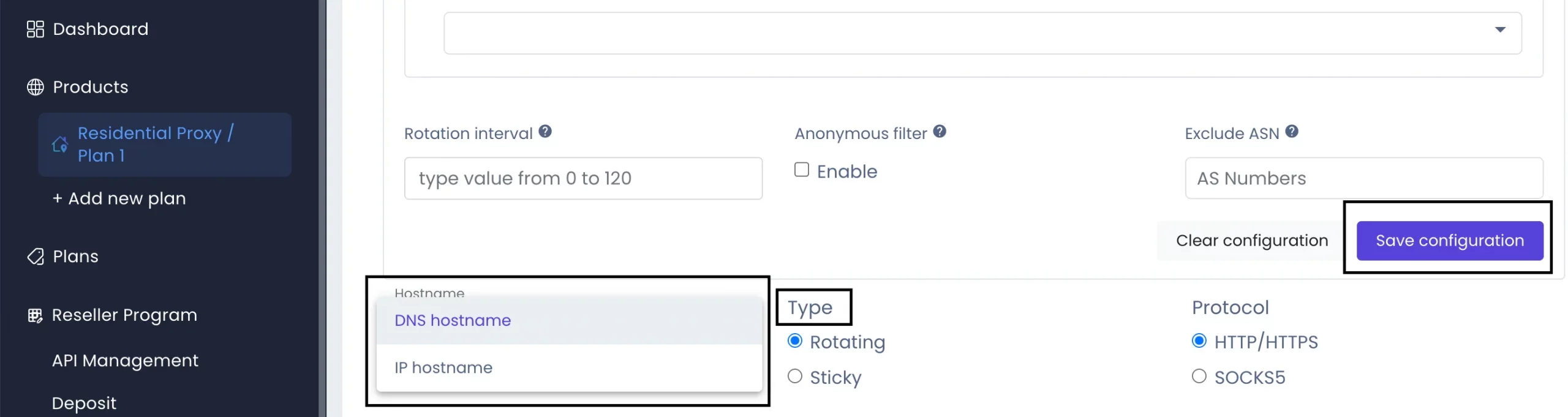
If you’re using DataImpulse, you might come across the IP hostname, which refers to one of the servers we offer. While it’s uncommon, there are times when load balancing may not function properly, directing requests to the wrong server. In these instances, users need to manually set up the proxy and choose the IP address of a server from a specific country that suits their needs. Additionally, some applications don’t support DNS hostnames and require the IP format instead.
✅ Advantages:
- Faster response with direct connection. Moreover, a direct connection can minimize the chances of external DNS issues.
- Operating in line with DNS filtering. For example, users in China can use IP hostnames to access our proxies.
- No need for DNS resolution. This can speed up connections since it eliminates the extra step of DNS lookup.
❌ Disadvantages:
- Manual configurations. If the IP address changes or gets blocked, the user would need to manually update their connection settings.
- Geo Load balancing is not supported. Without it, traffic is not routed based on the user’s geographical location. As a result, users may experience delays or increased latency if the server handling their requests is far from their location.
A consistent IP is important for tasks like account management to prevent connection interruptions, security systems for trusted connections, and banking services to prevent fraud alerts. It is also a great option for people who work remotely.
Host vs Direct IP connection
| Feature | Host | Direct |
| Stability | Stable | Depends on the IP server load |
| Ease of Setup | Easy to configure with a domain-based system | Direct IP configuration |
| Anonymity | Better anonymity with rotating IPs | Less anonymity, as a fixed IP can be tracked |
| Flexibility | High | Low |
| Speed | Slight delays due to the DNS resolution | Fast connections |
When using a DNS host or numerical host, the proxy service will automatically select the best possible route for the user’s request based on network optimization. This means that the proxy list will still be the same, but the DNS host dynamically determines the most efficient path for data transmission.
On the other hand, a direct connection to an IP address means that each proxy IP will be used without any intermediary host. This creates a fixed route for each request and does not involve dynamic optimization like DNS hosts.
The Reason Behind a Static Proxy List
Many DataImpulse users wonder why their proxy list stays the same and doesn’t change IPs. The proxy list is mainly created for sticky proxies because they remain fixed for a while, allowing multiple requests to be made without changing the IP. On the other hand, rotating proxies still change the IP address with every request, but the proxy list remains unchanged.
When you log into your DataImpulse dashboard, you can typically choose whether to use a DNS hostname or IP hostname in your proxy setup. Some applications may not work well with DNS-based hostnames like gw.dataimpulse.com and need to connect to the server using an IP address directly. This is because each time a proxy request is made, it may route from a different IP address, but with an IP address, the server is consistent for each request.
At Dataimpulse, we currently offer options with DNS and numerical hosts, but we do not provide a direct connection to proxy IP addresses. This may raise questions among some users who are accustomed to services that offer this kind of direct connection. However, for those looking for this specific option, it’s important to note that our DNS-based service still ensures optimal routing for proxy traffic, which ensures performance and stability.
If you want a different IP, it’s important to activate the rotation feature by selecting “Rotating” as the proxy type. Want to know more about rotating or sticky proxies? Here’s an insightful article.
We offer you a pool of more than 15 million IPs from 194 locations. If you have any additional questions, our 24/7 professional human support team is here to help you.