In this Article
5.3 billion users surf the web, each with a unique request. Now imagine a world without the internet – no Google, no YouTube, no online shopping. It’s hard to even think about, right? The internet has become a huge part of our lives, helping us learn, work, and stay connected. But have you ever wondered how it all works? How does a click on a link lead to a webpage appearing on your screen? Let’s take a closer look at this process together.
In this article, we’ll consider internet elements like IPs, DNS, HTTP, servers, and data centers to better understand aspects that shape our online world.
Internet 101: Back to Basics
The internet connects devices worldwide using special rules called protocols. These rules make sure data travels safely and reaches its destination.
Believe it or not, the Internet is just a wire hidden in the ground. In essence, the Internet includes routers, which direct data between devices. When you send something online, it’s split into small parts called packets and sent through routers until it gets where it needs to go.
Key protocols like IP and TCP help with this. IP gives each device a unique address, while TCP makes sure data is transmitted in the right order.
Other important things include DNS, which changes website names into numbers, and HTTP, which makes communication between web servers and browsers possible.
Such elements as routers, switches, and servers are linked by cables and wireless connections.
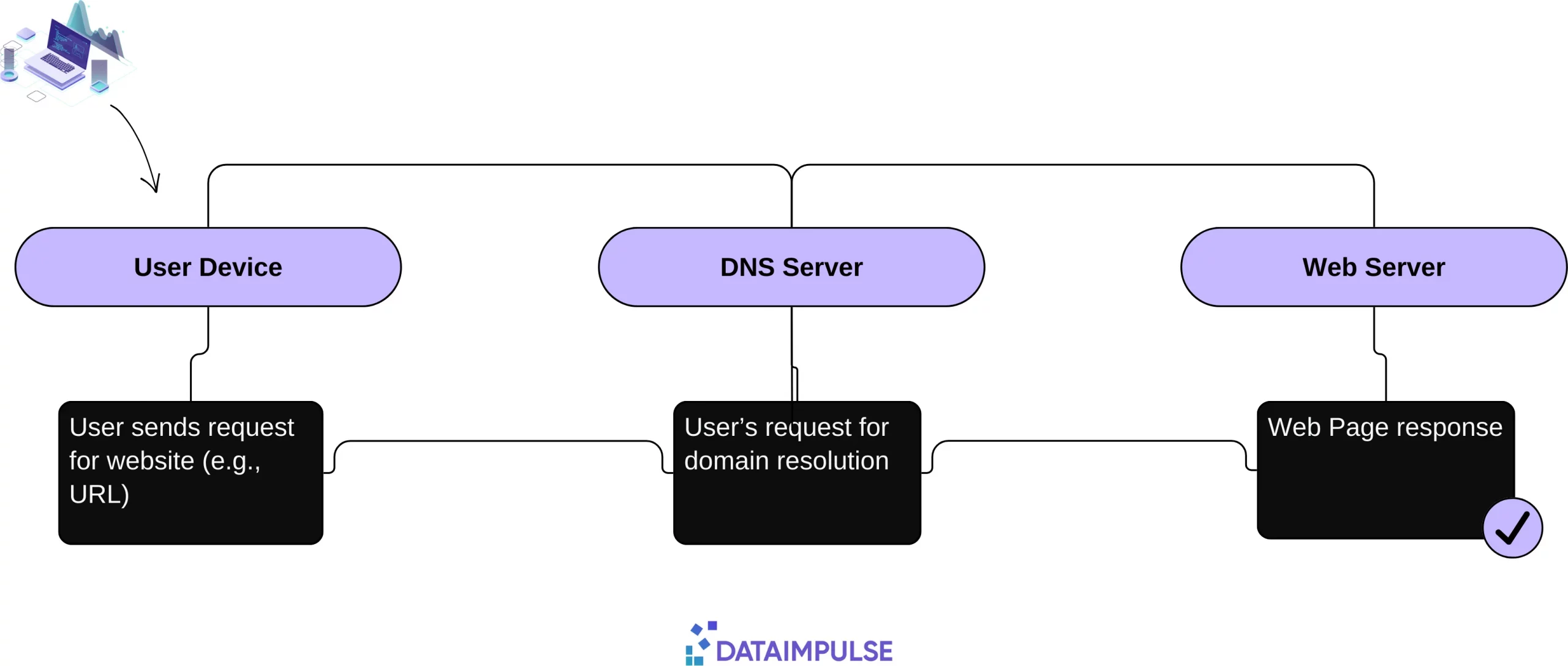
Here you can see a simple diagram that shows the flow of information from a user’s device to a website’s server:
DNS(Domain Name System)
When you want to visit a website, you often start by typing a domain name into your browser’s address bar. Domain names are human-readable names used to identify websites and other internet resources. They usually consist of two or more parts, separated by periods. For instance, “microsoft.com” is a domain name. DNS is responsible for translating domain names into IP addresses.
If you type a domain name into your web browser, your device sends a request to a DNS server, which then provides the matching IP address. Your device uses this IP address to make a connection with the desired website. Once a server containing the IP address information is located, it returns this information to the web browser. Subsequently, the browser seeks data about the website from the hosting server of the domain.
The hosting server keeps all the website’s data, encompassing files, databases, and HTML code. Upon receiving data from the hosting server, the web browser transforms it into a web page so users can access and view online content.
IP addresses: Overview
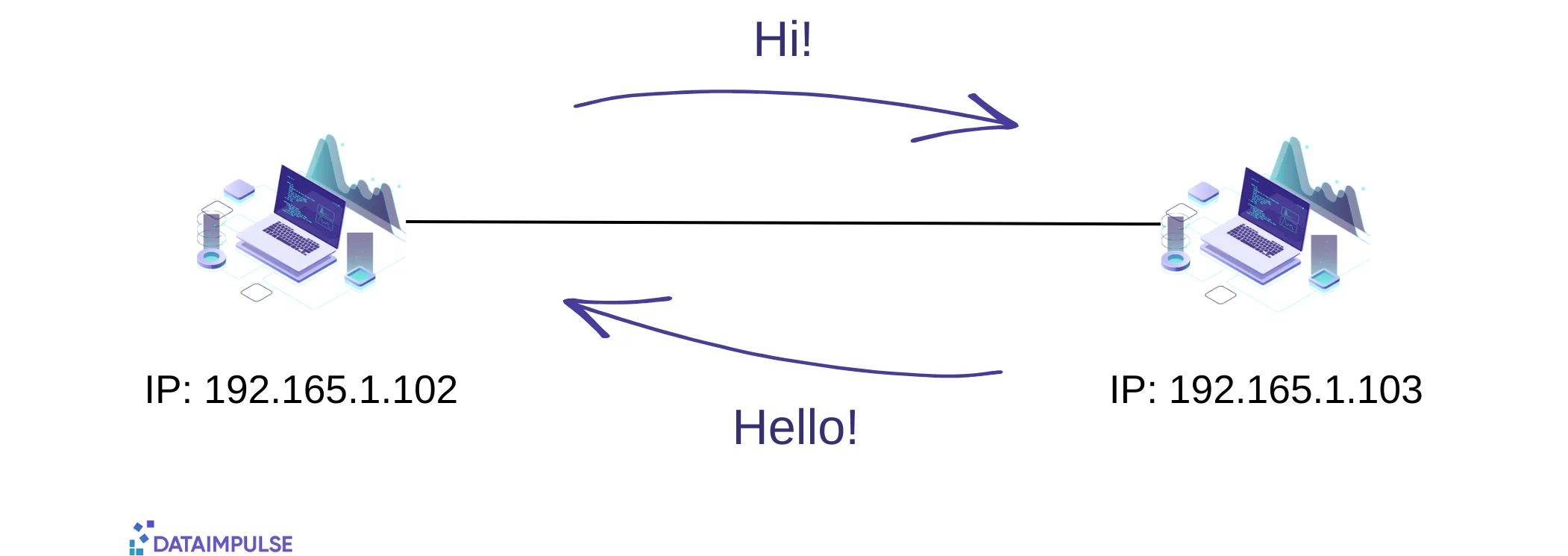
Every gadget is assigned an IP address. IP stands for Internet Protocol which is a set of rules setting the format of data sent via the Internet. These addresses work as digital tags, showing the origins and destinations of data packets. When your friends want to get in touch with you online, your computers rely on each other’s IP addresses to make sure your messages reach the intended destination.
IP addresses are usually represented as a set of four numbers separated by periods. The numbers can range from 0 to 255.
The easiest method to find your router’s public IP address is by typing “What is my IP address?” into the Google search bar. Google will show you the answer at the top of the search results page. Finding your private IP depends on the platform you use.
- Windows: Search for cmd in Windows search and in the Command Prompt window, type ipconfig.
- Mac: Go to System Preferences, Select Network, and view the information.
What’s the difference between a domain name and an IP address? Think of your domain name like the name of your shop – it’s what people recognize and remember. Your IP address is more like the shop’s location on a digital map.
When your business grows and moves to a larger location but keeps the original name, your website may need a bigger server while still using the same domain name. Keeping domain names and IP addresses separate makes upgrading easier without confusing the visitors.
Another important aspect is understanding how to properly protect your IP address. There are always security risks such as hacking, tracking your location, downloading illegal content with your IP, or even online stalking. So how can you protect and hide your IP address? Here are some of the main tips:
- Use Proxy Servers: they hide your IP address and provide a high level of anonymity;
- Use VPN (Virtual Private Network): VPN encrypts your internet connection and routes it through a safe server;
- Update Security and Antivirus Software Regularly: to make sure your operating system will be able to stay resilient against emerging threats;
- Be careful with Sharing Personal info: avoid sharing sensitive personal information online, especially on forums or social media platforms, to lower the risk of cyberstalking.
- Create Unique Passwords and Stay Alert to Phishing Emails
HTTP vs TCP
HTTP, or Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is a protocol used for transferring web pages and other resources on the Internet. When you enter a URL into your web browser, you send an HTTP request to a web server, which responds using the HTTP format. The web server then processes the request and sends back the requested webpage as an HTTP response. The “S” in HTTPS stands for “secure,” indicating that the packets are encrypted for better security.
TCP, or Transmission Control Protocol, is a protocol used for reliable communication over the Internet. It breaks data into small packets, sends them from Point A to Point B in a correct order and without errors. TCP uses a technique known as positive acknowledgment with retransmission. As a result, the bytes sent match the bytes received, no data is lost. TCP prioritizes reliability over speed, it sacrifices some speed to ensure the quality of the transmitted data.
The main difference between HTTP and TCP lies in their functions and purposes. HTTP is a higher-level protocol used specifically for transferring hypertext documents, such as web pages, between clients and servers on the internet. TCP is responsible for establishing and maintaining connections between devices, ensuring the reliable transmission of data packets. While HTTP focuses on the content and structure of web pages, TCP handles the communication mechanisms necessary for data transfer.
Inside Servers and Data Centers
A server stores, processes, and distributes information to other computers, referred to as clients, when requested. The tasks can include accessing websites, sending emails, or watching videos. Servers come in various shapes and sizes, from small-scale units used by individuals or businesses to large-scale server farms maintained by tech giants like Google, Amazon, or Facebook.
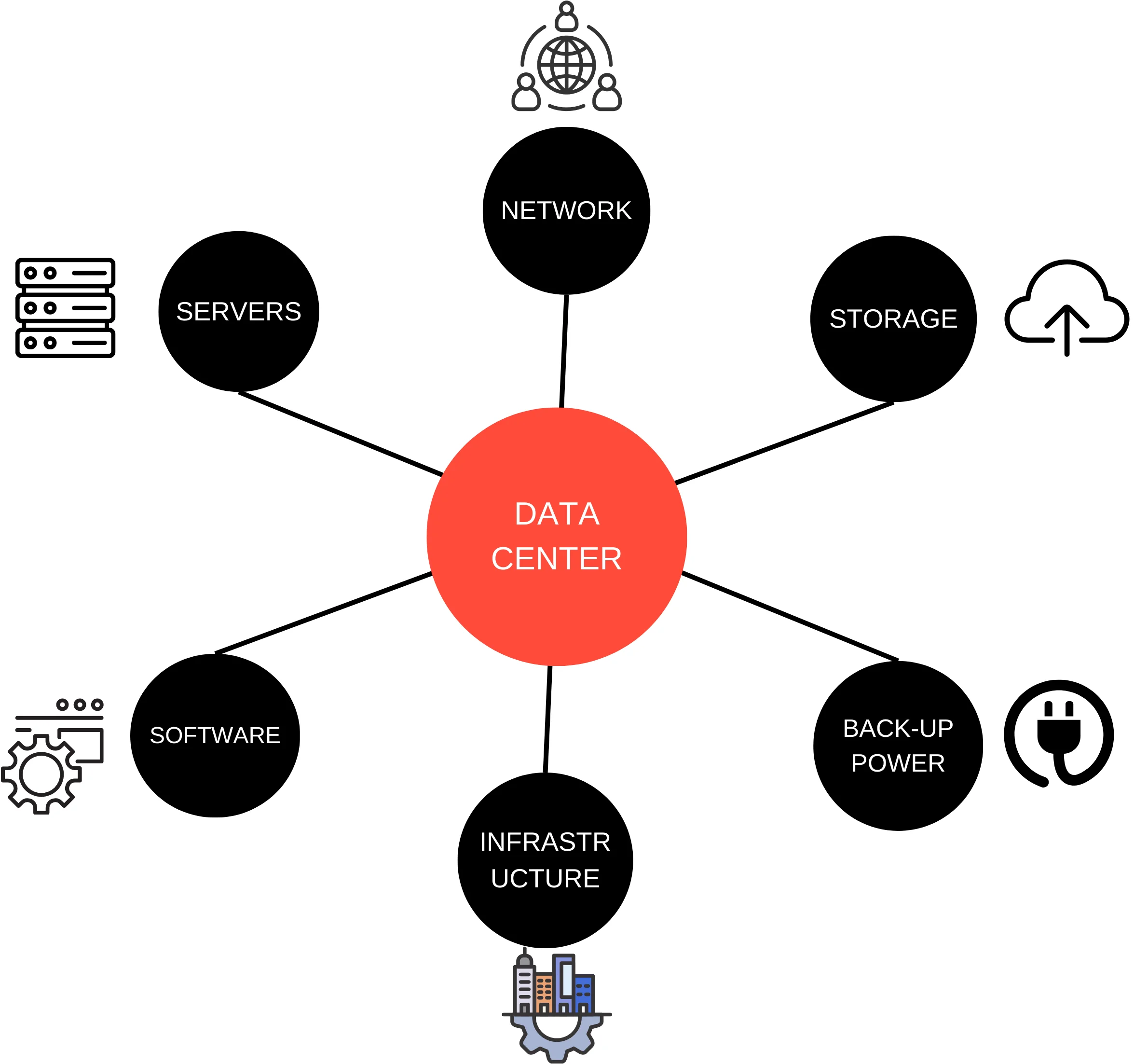
Data centers store servers, as well as networking equipment and storage systems, in one central facility. They are equipped with redundant power supplies, cooling systems, and network connections to lower the chances of downtime and maintain stable operation.
Inside a data center, servers are organized into racks with multiple server units stacked vertically. The servers are interconnected through high-speed networking infrastructure. Data centers use advanced management systems to control server performance, distribute resources effectively, and address any problems immediately.
After all, a server is like a computer or a program that completes tasks for you, while a data center is a big building full of servers and related equipment. They store and analyze large quantities of data, so we can effectively use online services and applications such as social media or e-commerce platforms.
Conclusion
At the heart of the internet, there is a complex network of protocols, servers, and data centers to facilitate communication and data exchange across the globe. Protocols like TCP/IP and HTTP manage the transmission and interpretation of data that is so important for online interactions.
In our digital world, safety is key. DataImpulse provides ethical residential, datacenter, and mobile proxies. Our service offers a pool of reliable IPs. Easily use our interface and get 24/7 human support for any questions.
Keep your secrets safe with DataImpulse. Join us by clicking the “Try now” button in the top-right corner.