In this Article
Companies like Amazon, eBay, and LinkedIn depend on web crawling as a fundamental data technique. They collect market trends, track pricing, and monitor competitor activity every day. For example, e-commerce platforms use crawlers to scan thousands of product pages daily to make sure they are competitive, and their products stay in demand.
Everyone who needs to process a mass of online content should have a web crawler. Tool selection depends on your goals: some prioritize large-scale distributed crawling, others excel at handling JavaScript-heavy websites, and the latest AI-driven crawlers can adapt to complex page layouts. In this article, we review versatile solutions suitable for a wide range of tasks in 2026.
*Web scraping and crawling should always be performed within legal and ethical boundaries. We do not encourage illegal activity and highlight only responsible usage strategies.
Top Open-Source Crawlers
1. Scrapy
Scrapy is a Python-based framework for engineering custom data crawlers. Supports asynchronous requests, extensible middleware, and integration with headless browsers. It extracts data by using CSS selectors and XPath expressions.
Key capabilities & Client advantages:
Scrapy offers fast, flexible scraping and parsing, with request scheduling, user-agent rotation, and rate-limiting. It integrates with headless browsers and AI-driven parsing tools. Scrapyd, a system that runs and controls spiders, occupies the central place in the Scrapy environment. This app is ideal for developers who want a highly customizable, Python-friendly solution.
Possible issues:
- Requires programming knowledge;
- Extra setup needed for JavaScript-heavy websites.
Install Scrapy and integrate DataImpulse proxies, check how.
2. Crawlee
Crawlee is a modern open-source competitor to Scrapy, built on Node.js/TypeScript (with growing Python support). It offers a unified API for both HTTP and full-headless browser crawling.
Key capabilities & Client advantages:
Its major advantage is the native integration of Playwright and Puppeteer. With this feature, developers can scrape dynamic, JavaScript-heavy websites without complex middleware setup. Crawlee also includes built-in features for proxy rotation, session management, and auto-scaling. It works quickly and is more resilient for modern web scraping compared to traditional frameworks.
Possible issues:
- Requires Node.js knowledge;
- Resource usage grows with concurrency and browser automation;
- Not ideal for extremely large, distributed crawling without additional infrastructure.
Parsing & Browser Automation Libraries
The next part of our list shows you not full crawlers on their own. These are indispensable libraries for building blocks for web crawlers.
3. Cheerio
It is a fast, lightweight JavaScript library for parsing and manipulating HTML on the server side.
How it works as a crawler: Cheerio loads HTML content and allows you to query elements using CSS selectors, similar to jQuery.
Benefits: extremely fast and efficient; ideal for static pages or lightweight scraping; can parse nearly any HTML or XML document; simple syntax for extracting structured data.
Issues: cannot render JavaScript, so dynamic content is inaccessible; needs additional tools for HTTP requests and large-scale crawling.
4. BeautifulSoup
It is a user-friendly Python library for parsing HTML and XML documents. It’s ideal for extracting web data without browser automation.
How it works as a crawler: BeautifulSoup processes HTML/XML responses from HTTP requests, providing a robust API for navigating the DOM tree and extracting elements programmatically.
Benefits: easy to learn and use; excellent for static pages and well-structured HTML; integrates well with Python requests or Scrapy.
Issues: cannot execute JavaScript; slower on extensive datasets compared to some JavaScript libraries.
5. Puppeteer
It is a Node.js library for controlling headless Chrome or Chromium browsers. Developed by Google, it excels at automating browser interactions. Puppeteer can crawl single-page applications (SPAs) and generate pre-rendered content.
How it works as a crawler: Puppeteer renders pages like a real browser, executes JavaScript, and exposes the DOM for scraping or automation tasks.
Benefits: dynamic, JS-heavy websites management; screenshots, PDFs, and full browser automation support; can emulate mobile devices and other user agents.
Issues: heavier and slower than simple parsers; requires more system resources; complex setups for intensive crawling.
6. Playwright
Developed by Microsoft in 2020, it is a modern automation framework for reliable end-to-end testing and web scraping across multiple browsers. As a successor to Puppeteer, it supports Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit through a unified API and runs tasks out-of-process to avoid common automation limitations.
How it works as a crawler: Playwright renders pages like a real browser, executes JavaScript, and simulates user interactions to extract dynamic content.
Benefits: cross-browser support, auto-waiting to avoid manual timeouts, a powerful selector engine for shadow DOM and iframes, mobile emulation, network interception, geolocation and permission mocking, multiple isolated browser contexts, and full headless or headed mode support.
Issues: higher resource usage compared to lightweight parsers due to full browser instances; slower than simple HTML-only solutions for very large-scale scraping.
Top AI-driven web crawlers
7. Crawl4AI
It is an open-source Python tool and AI-powered crawler that automatically interprets website structures and extracts data. It uses ML models to detect patterns in HTML and JavaScript, dynamically identifying relevant content.
Key capabilities & Client advantages:
Crawl4AI uses AI to detect content on complex pages and adapt to changing layouts. It specializes in LLM-ready data conversion, using AI to transform raw HTML into clean, structured formats like Markdown or JSON. This capability provides high-quality, noise-free input, which is essential for effective Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and model fine-tuning. Crawl4AI is ideal for both small and large-scale data extraction. With this crawler, clients focus on insights rather than maintaining scraping rules.
Possible issues:
- May require subscription for more features;
- Less control over low-level crawling parameters.
8. ScrapeGraphAI
It is a unique open-source library that empowers users to generate and execute complex scraping pipelines entirely through Natural Language Prompts. It analyzes DOM and page content to create extraction schemas, learning from previous runs to improve accuracy.
Key capabilities & Client advantages:
This app is suitable for non-technical users. Its main advantage is drastically reducing development time, so users can quickly create resilient scrapers by describing the data they want rather than manually writing complex selectors and logic.
Possible issues:
- Paid platform; free features may be limited;
- Performance can vary on heavily dynamic sites.
9. Diffbot
It’s a commercial, enterprise-grade service that uses advanced AI and computer vision to automatically extract data and keep scrapers working even when websites change.
Key capabilities & Client advantages:
Clients benefit from unmatched scalability and robustness, as the platform maintains high extraction accuracy across ever-changing website layouts without requiring manual updates or infrastructure management. For easy integration, it is cloud-based with APIs.
Possible issues:
- Paid service; can be expensive for large-scale crawling;
- Less flexible for highly customized crawling scenarios.
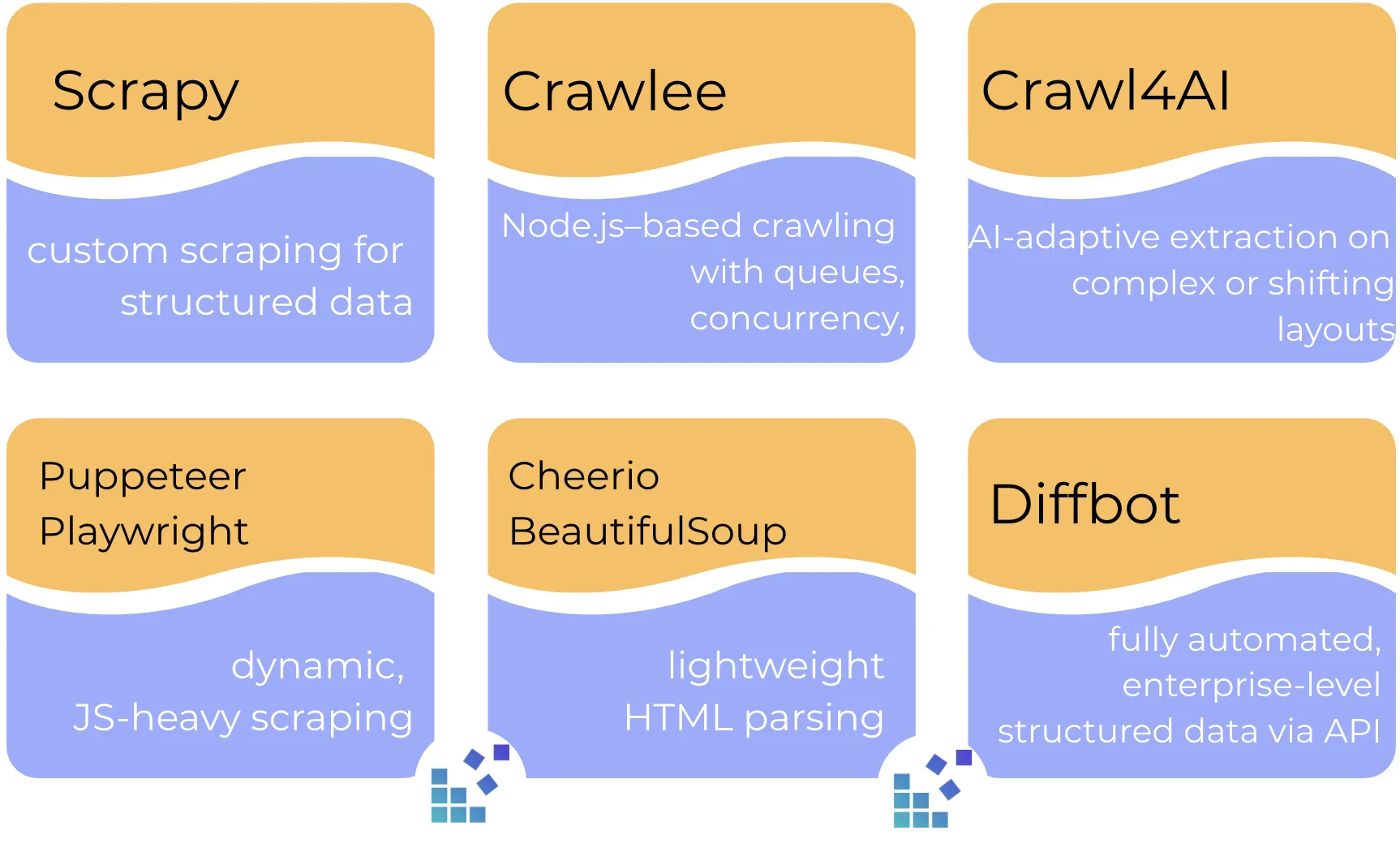
If you’re unsure which crawler fits your use case, this table provides a quick breakdown to help you decide.
To improve your Crawler Performance, include:
There is always some content that can’t be so easily accessed. Users experience access interruptions for their numerous attempts. With our proxies, such unfavorable actions will be reduced to a minimum. Proxies are widely used for web scraping or web crawling. They work by managing requests across multiple IPs for you to enjoy local content. Thus, it’s great for accurate region-specific data extraction.
- Headless browser rendering
A significant number of modern sites today rely on JavaScript. Rendering with Playwright or Puppeteer recreates a real browser environment. This way, a crawler can accurately extract the DOM and handle obfuscated client-side code.
- AI-driven parsing
LLM-powered extractors analyze a page by understanding structure, semantics, and context. Instead of relying on fragile CSS or XPath selectors, they interpret layouts, adapt to design changes, and extract data even when the HTML structure shifts.
- Captcha solvers
A CAPTCHA is a human-verification mechanism that distinguishes humans from automated systems and stops unwelcome bot activity. Automated solvers or API-based services help maintain crawl continuity when sites deploy human-verification layers during high-volume scraping.
- Rate-limiting logic
Rate limiting is a technique for regulating the number of requests a crawler or user can make to a server within a specific time window. Controlling how often requests are sent to a website prevents server strain. It makes your traffic behave like a normal user and works hand in hand with proxies to maintain a low profile within the system.